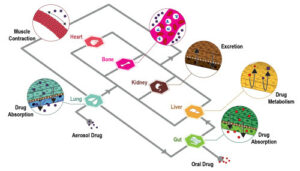
Why a pancreas on a chip?
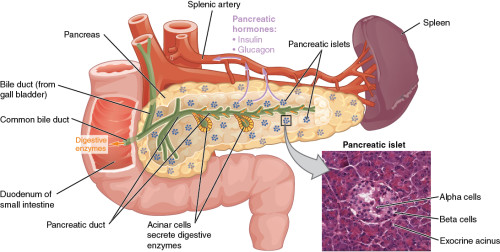
The pancreas is an annex gland of the digestive system. It has both endocrine and exocrine functionality. Its exocrine function consists of the secretion of digestive fluids containing enzyme facilitating the digestion of fatty acids. Its endocrine function is based on hormone secretion that regulates glycemia (insulin, glucagon). Pancreas cancer is generally associated with bad prognostic, thus there a real need for new therapies.
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
What has already been achieved ?
Preamble: type 1 diabetes is an auto-immune disease characterized by the destruction of Langherans β islets. The only one treatment (except symptomatic ones) is the islet transplantation, but these treatments often fail due to cellular damage linked to the islet isolation process, hypoxia….
A Michigan University team (Kennedy Robert T team (1)) created a PDMS chip allowing the assessment of 15 mice islets individually based on their insulin secretion. Authors consider the use of this pancreas on a chip to investigate the fundamental origin of type 1 diabetes and to improve the success rate of the islet transplantation (by monitoring the islet function and so only select the healthy one for transplantation).
Oberholzer, wang, and Nourmohammadzadeh in Chicago University developed a platform allowing the culture and real-time imaging of pancreatic islets encapsulated in a hydrogel (2). The chip is made in PDMS thanks to soft lithography techniques. The chip is specifically designed to trap and encapsulate individual rats or human islets. Authors challenged the system with hypoxia and observed significant changes in signalization pathways of islets. This device might be used to study both the mechanism of transplantation failure and macrophages-islets interactions.
Lin P team in Shandong University developed a pancreas-on-a-chip allowing co-culture and communication of bone marrow and pancreatic cells (3). This device enables the study of processes dynamic that underlie the migration of stem cells from bone marrow to the pancreatic islet. Authors quantify the islet response by the level of insulin secretion following hyperglycemia stimuli.
A Korean team has developed a chip for the co-culture of islets and fat tissue spheroids. The chip is composed of microwells in which co-cultures are inserted (coming from rat) (4). Authors found that the co-culture of islet and fat spheroids increases the survivability of islets and thus the potential success rate of transplantation.
Park S team in Seoul built a pancreas on a chip with interconnections between pancreatic islets and gut cells and measure the insulin secretion of β islets (5). Both in normal and diabetes-like conditions, the system reacts as expected. It highlights the potential of this model to mimic diseases and so to be involved in the drug development process for new anti-diabetes drugs.
TissUse Company has developed a platform allowing the culture of 2 or 4 organs on a chip. They evidenced communication between liver and pancreas (using their 2 organs-on-chip system): the liver regulates the insulin production of the pancreas.
What’s next in the organ on chip pancreas field?
Despite many improvements, up to days, it is impossible to recreate both the endo and exocrine function of the pancreas at the same time. Furthermore, the ductal compartment of the pancreas has never been recreated on a chip.
References
1: Anal Chem. 2009 Apr 15; 81(8): 3119–3127. doi: 10.1021/ac900109t. Quantitative Monitoring of Insulin Secretion from Single Islets of Langerhans in Parallel on a Microfluidic Chip. John F. Dishinger Kendra R. Reid, and Robert T. Kennedy
2: Anal Chem. 2013 Dec 3;85(23):11240-9. doi: 10.1021/ac401297v. Epub 2013 Nov 15. Microfluidic array with integrated oxygenation control for real-time live-cell imaging: effect of hypoxia on physiology of microencapsulated pancreatic islets. Nourmohammadzadeh M1, Lo JF, Bochenek M, Mendoza-Elias JE, Wang Q, Li Z, Zeng L, Qi M, Eddington DT, Oberholzer J, Wang Y.
3: Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2009;30(2):204-8. Dynamic analysis of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells migrating to pancreatic islets using coculture microfluidic chips: An accelerated migrating rate and better survival of pancreatic islets were revealed. Lin P1, Chen L, Li D, Yang N, Sun Y, Xu Y
4: Biomaterials. 2014 Jun;35(17):4815-26. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2014.02.045. Epub 2014 Mar 15. Microchip-based engineering of super-pancreatic islets supported by adipose-derived stem cells. Jun Y, Kang AR, Lee JS, Park SJ, Lee DY, Moon SH, Lee SH
5: Biofabrication. 2017 Feb 21;9(1):015021. doi: 10.1088/1758-5090/aa5cc9. Endocrine system on chip for a diabetes treatment model. Nguyen DT1, van Noort D, Jeong IK, Park S.