Introduction
Organ-on-Chips for Studying Tissue Barriers – Disruption of cell-formed tissue barriers is an essential part of many diseases’ pathophysiology. Therefore, a thorough understanding of tissue barrier function is essential when studying the causes and mechanisms of disease as well as when developing novel treatments.
In vitro methods play an integral role in understanding tissue barrier function, and several techniques have been developed in order to evaluate barrier integrity of cultured cell layers, from microscopy imaging of cell-cell adhesion proteins to measuring ionic currents, to flux of water or transport of molecules across cellular barriers. Learn how the authors use Organ-on-a-chip for studying Tissue Barriers below –
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract
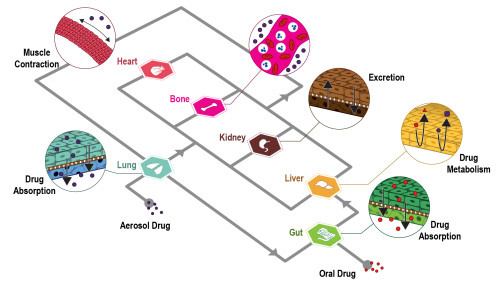
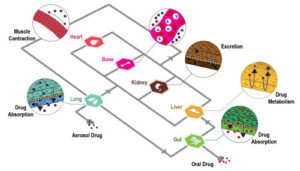
The authors state that “A relevant number of organ-on-chips is aimed at modeling epithelial/endothelial interfaces between tissue compartments. These barriers help tissue function either by protecting (e.g., endothelial blood-brain barrier) or by orchestrating relevant molecular exchanges (e.g., lung alveolar interface) in human organs.
Models of these biological systems are aimed at characterizing the transport of molecules, drugs, or drug carriers through these specific barriers. Multilayer microdevices are particularly appealing to this goal and techniques for embedding porous membranes within organ-on-chips are therefore at the basis of the development and use of such systems.
Here, we discuss and provide procedures for embedding porous membranes within multilayer organ-on-chips. We present standard techniques involving both custom-made polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) membranes and commercially available plastic membranes. In addition, we present a novel method for fabricating and bonding PDMS porous membranes by using a cost-effective epoxy resin in place of microfabricated silicon wafers as master molds.”
References
Ballerini M, Jouybar M, Mainardi A, Rasponi M, Ugolini GS. Organ-on-Chips for Studying Tissue Barriers: Standard Techniques and a Novel Method for Including Porous Membranes Within Microfluidic Devices. Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2373:21-38. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-1693-2_2. PMID: 34520004.
FAQ
The disruption of tissue barriers formed by cells is an element in the pathophysiology of many diseases. A complete understanding of how these barriers function is therefore required. This understanding is needed when studying the causes and mechanisms of a disease. It is also necessary when new treatments are being developed. In vitro methods are integral to gaining this understanding of tissue barrier function. Several techniques have been created to evaluate the integrity of cell layers grown in culture. These include microscopy imaging of cell-cell adhesion proteins. Other methods involve measuring ionic currents or the flux of water. The transport of molecules across cellular barriers can also be measured.
A relevant number of organ-on-chip systems are designed to model the interfaces between tissue compartments. These interfaces are often epithelial or endothelial barriers. These barriers assist tissue function in human organs. This can be by providing protection, such as the endothelial blood-brain barrier. They can also work by orchestrating molecular exchanges, like the lung alveolar interface. Models of these biological systems are intended to characterise transport through these specific barriers. The transport of molecules, drugs, or drug carriers is what is studied. Multilayer microdevices are particularly well-suited for this objective.
Techniques for embedding porous membranes within organ-on-chips are a fundamental part of the development and use of such systems. These systems are often multilayer microdevices. This structure is advantageous for modelling biological barriers, such as epithelial or endothelial interfaces. The porous membrane is used to separate the different tissue compartments. This arrangement allows for the study of transport from one compartment to another, through the cellular barrier that is cultured on the membrane. The paper discusses and provides procedures for placing these membranes within multilayer organ-on-chips. Both standard techniques and new methods are presented.
In addition to standard techniques, a new method is presented. This method is for fabricating and bonding porous membranes made of PDMS (polydimethylsiloxane). Standard techniques are also discussed in the paper. These involve either custom-made PDMS membranes or commercially available plastic membranes. The new method is different because it uses a cost-effective epoxy resin. This resin is used in place of microfabricated silicon wafers. These wafers traditionally act as the master molds. This new procedure is presented as an alternative way to embed porous membranes within multilayer organ-on-chip devices.