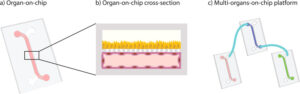
Introduction
MPS (Multiorgan Microphysiological Systems) have evolved from tools to reduce animal experimentation and improve preclinical toxicity assessments to an intriguing stepping stone in efforts to replicate our own biology. The future premise of MPS is clear: multicellular tissue models that are true to our own physiology would allow us to conduct expensive clinical trials at a fraction of the cost.
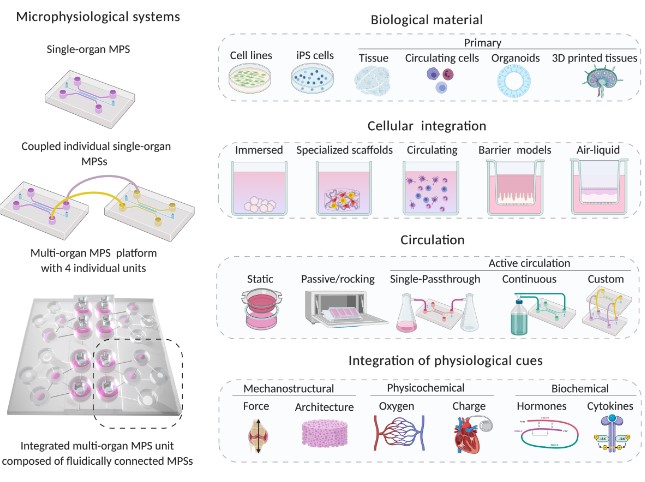
Reduce the use of animals in experiments, serve as a surrogate for exploring the dangers of new environments such as deep space, and provide insight into the laws governing tissue homeostasis, repair, and the emergence of complex diseases, to name a few. While this may sound like a pipe dream, it is a reality that the field is gradually achieving.
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract
The author states that “Metabolic and inflammatory disorders such as autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases are increasing at alarming rates. Many of these are not tissue-specific occurrences but complex, systemic pathologies of unknown origin for which no cure exists.
Such complexity obscures causal relationships among factors regulating disease progression. Emerging technologies mimicking human physiology, such as microphysiological systems (MPSs), offer new possibilities to provide clarity in systemic metabolic and inflammatory diseases.
Controlled interaction of multiple MPSs and the scalability of biological complexity in MPSs, supported by continuous multiomic monitoring, might hold the key to identifying novel relationships between interorgan crosstalk, metabolism, and immunity.
In this perspective, I aim to discuss the current state of modeling multiorgan physiology and evaluate current opportunities and challenges.”
References
Trapecar M. Multiorgan Microphysiological Systems as Tools to Interrogate Interorgan Crosstalk and Complex Diseases. FEBS Lett. 2021 Dec 18. doi: 10.1002/1873-3468.14260. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 34923635.
FAQ
MPS, or Multiorgan Microphysiological Systems, are tools that have developed over time. They were first used to lessen the number of animal experiments and to enhance preclinical toxicity assessments. Their purpose has expanded, and they are now considered a step towards recreating human biology. The main objective is to create multicellular tissue models that accurately represent human physiology. If successful, these models could allow expensive clinical trials to be performed at a much lower cost. This goal is being approached by the field, although it has not been fully met. MPS are seen as one way to better understand biological processes without using animal models.
Multiorgan Microphysiological Systems have several possible uses. A primary goal is to reduce the reliance on animals for experiments. They may also act as a substitute model for studying the dangers of new environments, such as deep space exploration. Beyond this, MPS could provide information on the principles that control tissue homeostasis and repair. Another suggested application is for gaining a better understanding of how complex diseases emerge. These systems are being developed to model human biology more closely. The development of multicellular tissue models that reflect our physiology is the main aim. These systems offer a new way to study complex biological questions.
New models are required because metabolic and inflammatory disorders are increasing. This includes conditions such as autoimmune and neurodegenerative diseases. Many of these illnesses are not specific to one tissue. They are instead complex, systemic problems. Currently, the origin of these pathologies is often unknown, and no cure exists. This complexity makes it difficult to see the causal relationships between the factors that regulate how a disease progresses. Better models are needed to understand these systemic and complex conditions. Standard approaches have not provided complete answers for these widespread health issues.
Microphysiological systems (MPSs) are new technologies that are designed to copy human physiology. They present new possibilities for bringing clarity to systemic metabolic and inflammatory diseases. The benefit of MPSs is the ability to have controlled interaction between multiple systems. The biological complexity within these systems can also be scaled. When this is supported by continuous multiomic monitoring, it may become possible to identify new relationships. These relationships could be between interorgan communication, the body’s metabolism, and immunity. This approach is being evaluated to understand its prospects and difficulties. The goal is to find connections that are hidden by the complexity of the diseases.