Discover new in vivo protocols to understand contractile ring dynamics during cytokinesis in C. elegans embryo
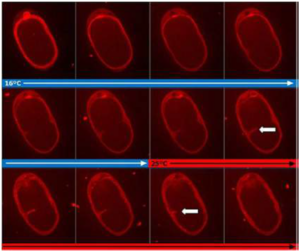
Fung Yi Chan, Ana Marta Silva, and Ana Xavier Carvalho elaborated several experimental approaches for monitoring contractile ring dynamics in 4 cell stage C. elegans embryo. Determinant during the cytokinesis, the actomyosin contractile ring is still not fully understood and the failure to set it up it could lead to tumorigenesis. The group has studied and established differents ways to disturbed the contractile ring such as drug treatments, thermosensitive mutants & fast temperature shifts, laser microsurgery and RNAi-meditated depletion. In this paper, you can find their approaches and the possibility to how they have live imaged the contractile ring dynamics during perturbations. Temperature-sensitive mutants experiments have been done using our CherryTemp device.
Ultra fast temperature shift device for in vitro experiments under microscopy
Abstract
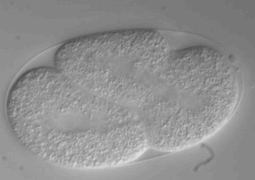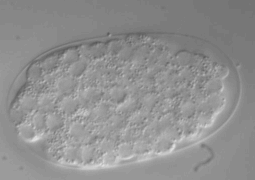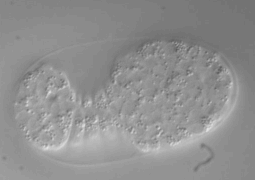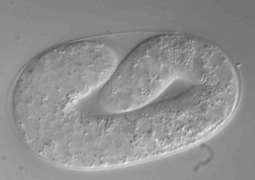
Cytokinesis is the process that completes cell division by partitioning the contents of the mother cell between the two daughter cells. It involves the highly regulated assembly and constriction of an actomyosin contractile ring, whose function is to pinch the mother cell in two. Research on the contractile ring has particularly focused on the signaling mechanisms that dictate when and where the ring is formed. In vivo studies of ring constriction are however scarce and its mechanistic understanding is therefore limited. Here we present several experimental approaches for monitoring ring constriction in vivo, using the four-cell C. elegans embryo as model. These approaches allow for the ring to be perturbed only after it forms and include the combination of live imaging with acute drug treatments, temperature-sensitive mutants and rapid temperature shifts, as well as laser microsurgery. In addition, we explain how to combine these with RNAi-mediated depletion of specific components of the cytokinetic machinery.
References
- Chan F.Y., Silva A.M., Carvalho A.X. (2020)
Using the Four-Cell C. elegans Embryo to Study Contractile Ring Dynamics During Cytokinesis. In: Maiato H. (eds) Cytoskeleton Dynamics. Methods in Molecular Biology, vol 2101. Humana, New York, NY
FAQ
Cytokinesis is the process that finishes cell division. It works by partitioning the contents of the mother cell into the two daughter cells. This process involves the assembly and constriction of an actomyosin contractile ring. The function of this ring is to pinch the mother cell in two. The contractile ring is a determinant component of cytokinesis. It is not yet completely understood. A failure in the correct setup of this ring could lead to tumourigenesis. Research has often been focused on the signalling mechanisms that control when and where the ring is formed.
The four-cell C. elegans embryo is used as a model organism. Researchers have established several experimental approaches for monitoring the dynamics of the contractile ring in this specific model. These approaches are used to study ring constriction in vivo. This is an important area of study because in vivo research on ring constriction is uncommon. As a result, the understanding of its mechanism is limited. The C. elegans model allows the ring to be perturbed after it has already formed. This permits a focused study of the constriction phase.
Several experimental approaches for monitoring ring constriction have been established. These methods allow the ring to be perturbed after it has formed. The approaches include the combination of live imaging with different types of disturbances. One method is the application of acute drug treatments. Another technique involves using temperature-sensitive mutants. These mutants are studied using rapid temperature shifts. Laser microsurgery is also used to disturb the ring. The development of new techniques has made it simpler for scientists to screen for temperature-sensitive C. elegans. This allows the role of specific proteins to be questioned.
The methods for studying the contractile ring can be used together. For instance, live imaging is combined with acute drug treatments, rapid temperature shifts, or laser microsurgery. This allows researchers to observe the ring’s dynamics while perturbations are occurring. Furthermore, these approaches can be combined with the RNAi-mediated depletion of specific components. This depletion technique is used to remove specific parts of the cytokinetic machinery. Using temperature-sensitive mutants with fast temperature shifts allows researchers to precisely question a protein’s role by observing what happens in its absence.