Immune checkpoint modulation in renal cell carcinoma
In this paper, Bedke and colleague highlight the way that patients treated for the metastatic disease in renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) by a cytokine treatment (cytokine Il-2 and IFN-α alone or combine with 5-Fluoracil) have experienced a disease stabilization or remission in up of 30% of the patients. But only for some months. It is a limited therapy due to the increase of regulatory T cells (Tregs and decreasing of circulating myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. In this paper, the authors highlight a new way to address renal cell carcinoma treatment targetting immune checkpoint modulation (PD-1, CTLA-4,…). They review the ongoing clinical data linked to the use of such immune checkpoint modulation pathway in the renal carcinoma.
Summary
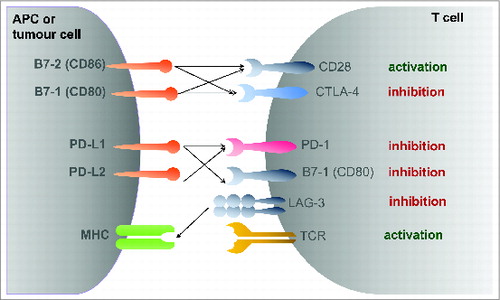
The introduction of targeted therapies like the tyrosine kinase (TKI) and mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) inhibitors has improved patients survival in general. Nevertheless, the prognosis remains limited. Therapies with a new mode of action are urgently warranted, especially those who would provoke long-term responders or long-lasting complete remissions as observed with unspecific immunotherapy with the cytokines interleukin-2 and interferon-a. In the recent years, a deeper understanding of the underlying immunology of T cell activation led to the development of checkpoint inhibitors, which are mainly monoclonal antibodies and which enhances the presence of the co-stimulatory signals needed for T cell activation or priming. This review discusses the clinical data and ongoing studies available for the inhibition of the PD-1 (CD279) and CTLA-4 (CD152) axis in mRCC. In addition, potential future immunological targets are discussed. This approach of T-cell activation or re-activation by immunological checkpoint inhibition holds the inherent promise to directly affect the tumor cell and thereby to potentially cure a subset of patients with mRCC.
References
LEARN MORE | Bedke, J., Kruck, S., Gakis, G., Stenzl, A., & Goebell, P. J. (2015). Checkpoint modulation – A new way to direct the immune system against renal cell carcinoma . Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics, 11(5), 1201–1208. https://doi.org/10.1080/21645515.2015.1016657
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
FAQ
Patients treated for metastatic renal cell carcinoma (mRCC) with cytokine treatments, such as Il-2 and IFN-$\\alpha$, experienced some positive outcomes. Disease stabilization or remission was seen in up to 30% of these patients. This effect, however, was a limited therapy because it only lasted for some months. The treatment’s effectiveness was restricted due to an increase in regulatory T cells, or Tregs. It also caused a decrease in circulating myeloid and plasmacytoid dendritic cells. While newer targeted therapies improved survival, the prognosis remained limited, creating a need for treatments that provoke long-term responses.
A new way to treat renal cell carcinoma is being investigated. This method involves targeting immune checkpoint modulation. The approach developed from a deeper understanding of the immunology of T cell activation. These therapies use checkpoint inhibitors, which are mainly monoclonal antibodies. The function of these inhibitors is to enhance the co-stimulatory signals that are necessary for T cell activation, also known as priming. This strategy of T-cell re-activation holds the promise of directly affecting the tumour cell. It may have the ability to potentially cure a subset of patients with mRCC.
The new approach for mRCC treatment involves targeting specific immune checkpoint pathways. Research is focused on checkpoint inhibitors that act on these pathways. A review of the topic discusses the available clinical data and ongoing studies for the inhibition of two main axes. The first is the PD-1 (CD279) axis. The second is the CTLA-4 (CD152) axis. Therapies that block these pathways are intended to enhance T cell activation, allowing the immune system to direct an attack against the tumour. Potential future immunological targets are also being discussed in addition to these.
While targeted therapies like TKI and mTOR inhibitors have improved patient survival, the prognosis for mRCC remains limited. Therapies with a new mode of action are urgently needed. Specifically, there is a need for treatments that would provoke long-term responders. The goal is to achieve long-lasting complete remissions. This type of durable response was sometimes observed with older unspecific immunotherapy using cytokines. The aim is to find a new approach that can reliably produce these long-term results. Immunological checkpoint inhibition is being studied as one such approach that holds this promise.