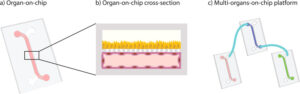
Introduction
DMS, often known as dimethylpolysiloxane or dimethicone, is a silicone polymer. There are various uses for PDMS owing to its flexibility and characteristics.
Although PDMS is a very good and practical solution while a small number of units are needed, industrialization and scaling up steps are hard to handle with this polymer.
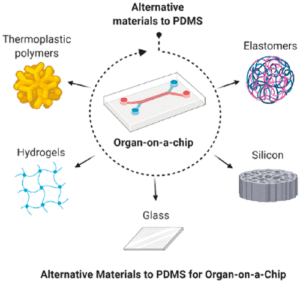
To prevent absorption, leaching, and autofluorescence or to facilitate quick prototyping, it may be necessary to fabricate the majority of the device with a material other than PDMS.
Hydrogel-based devices have also been developed as a result of advances in manufacturing processes (3D printing, for example). Learn more about the alternatives to PDMS in the paper below.
Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS): Alternative Materials
- Elastomers
- Thermoplastics
- Glass
- Silicone
- Adhesives or Epoxy Resins
- Hydrogels
- Paper based devices
How to culture vascularized & immunocompetent 3D models in a standard Multiwell
Abstract
The author states that” Polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) is the predominant material used for organ-on-a-chip devices and microphysiological systems (MPS) due to its ease-of-use, elasticity, optical transparency, and inexpensive microfabrication.
However, the absorption of small hydrophobic molecules by PDMS and the limited capacity for high-throughput manufacturing of PDMS-laden devices severely limit the application of these systems in personalized medicine, drug discovery, in vitro pharmacokinetic/pharmacodynamic (PK/PD) modeling, and the investigation of cellular responses to drugs.
Consequently, the relatively young field of organ-on-a-chip devices and MPSs is gradually beginning to make the transition to alternative, nonabsorptive materials for these crucial applications.
This review examines some of the first steps that have been made in the development of organ-on-a-chip devices and MPSs composed of such alternative materials, including elastomers, hydrogels, thermoplastic polymers, and inorganic materials. It also provides an outlook on where PDMS-alternative devices are trending and the obstacles that must be overcome in the development of versatile devices based on alternative materials to PDMS.”
References
Campbell SB, Wu Q, Yazbeck J, Liu C, Okhovatian S, Radisic M. Beyond Polydimethylsiloxane: Alternative Materials for Fabrication of Organ-on-a-Chip Devices and Microphysiological Systems. ACS Biomater Sci Eng. 2021 Jul 12;7(7):2880-2899. doi: 10.1021/acsbiomaterials.0c00640. Epub 2020 Sep 9. PMID: 34275293.